Utilising VLANs in OpenWRT
There are many ways you can utilise VLANs in OpenWRT. This documents particularly how to configure a TP-Link WDR4300 running OpenWRT 12.09 to conform to an existing VLAN topology, where VLAN 1 is for data and VLAN 2 is for VOIP (voice) traffic.
Create a third VLAN:
By default OpenWRT comes with VLANs disabled and when enabled, there are two VLANs. VLAN 1 is for the lan interface and VLAN 2 is for the wan interface. Here we have to enable VLANs, create a third VLAN and swap configurations between VLAN 2 and 3:
- Click on Network.
- Click on Switch.
- Select Enable VLAN functionality.
- Scroll down and click on Add - VLAN ID 3 should appear.
- Make VLAN 3 settings the same as VLAN 2
- Set CPU to tagged for VLAN 3
- Set Port 1 to off for VLAN 2
- Set Port 1 to untagged for VLAN 3
- Press Save
Re-Configure the WAN Interface
Now we need to tell the WAN interface to use VLAN 3 instead of VLAN 2:
- Click on Network.
- Click on Interfaces.
- Click on Edit for the WAN interface
- Click on Physical Settings
- In Interface select VLAN Interface: "eth0.3".
- Press Save & Apply.
- Check that wan is set to VLAN Interface: "eth0.3"
- Re-check the Switch settings are as per the previous section.
- Click on System then Reboot.
- Click on Perform reboot.
It can take about a minute for services to return after this reboot.
Create the Voice VLAN Interface
Welcome back! Hopefully you didn't make any typos and haven't had to factory reset the box once or twice to get here. Now we're going to create the interface for voice traffic:
- Click on Network.
- Click on Interfaces.
- Click on Add new interface...
- Name the interface appropriately, I'll use Voice for this example.
- Ensure the interface is set to Static address.
- Set Cover the following interface to VLAN Interface: "eth0.2".
- Press Submit.
You will now be taken to the page titled Interfaces - Voice.
Common Configuration
General Setup
Here we set the basic IPv4 configuration for this interface (did I mention I'm assuming IPv4?).
- Set the IPv4 address as appropriate.
- Select a class C netmask (255.255.255.0) if you have a class C network (most likely)
- Press Save.
Firewall settings
After clicking on the Firewall Settings tab, we will assign the Voice interface to the lan firewall zone:
- Select lan.
- Press Save.
DHCP Server
General Setup
I required a DHCP server for the VOIP handsets, so here's what we set:
- De-select Disable DHCP for this interface.
- Set the Limit to 100
- Press Save.
That's it. Everything else is automatically determined by the IPv4 address you set in Common Configuration. I set the limit 100 as that is the dedicated DHCP range for VOIP handsets on that LAN. You could probably safely leave it at 150 (the default) or set it to the range appropriate for your network.
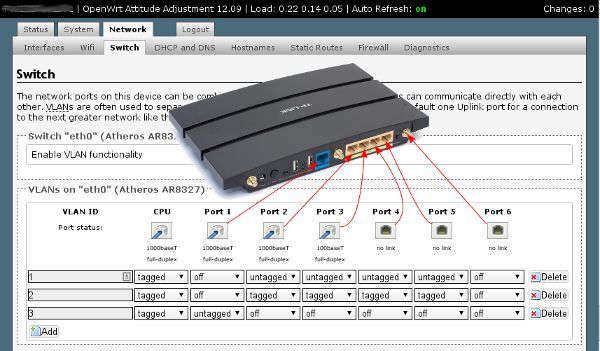
Switch Configuration
Now we need to tell the OpenWRT switch which ports will be active on the Voice VLAN. In this example I select all 4 LAN ports on the WDR4300:
- Click on Network.
- Click on Switch.
- Set Port 2 through to Port 5 as tagged for VLAN 2 (as per picture below)
- Press Save & Apply.
This picture illustrates the connection between switch ports in OpentWRT and the physical ports on the WDR4300, as well as the final switch configuration:
Send it live!
Okay, let's roill the dice and hope it comes back up:
- Click on System then Reboot.
- Click on Perform reboot.
If you've not made any typos, it should all came back up and you'll have a working VLAN 2 for voice. If you can't access the box, you've made typo. Factory reset and try again. Happy VLAN-ing!
